Reproductive Health Project PDF: A Comprehensive Guide
Reproductive health is an essential part of overall health and well-being. It refers to a state where people can have a safe and satisfying reproductive life. This includes the right to access safe and effective contraceptive methods, proper maternal healthcare, and protection from sexually transmitted diseases (STDs).
A Reproductive Health Project is a structured initiative designed to improve reproductive health services, create awareness, and provide healthcare support to people, especially women and young girls. These projects are run by governments, health organizations, and NGOs worldwide to ensure reproductive rights and health services for all.
2. Objectives of a Reproductive Health Project
The primary goal of a reproductive health project is to promote safe and healthy reproductive practices. Some key objectives include:
2.1 Improving Maternal and Child Health
- Ensuring pregnant women receive proper medical care before, during, and after childbirth.
- Reducing maternal and infant mortality rates.
- Promoting safe childbirth practices and hospital deliveries.
2.2 Providing Family Planning Services
- Educating people about different contraceptive methods.
- Making birth control accessible to all, especially in rural areas.
- Helping couples plan pregnancies according to their financial and health conditions.
2.3 Spreading Awareness on Reproductive Rights
- Educating people about their rights to reproductive healthcare.
- Empowering women to make informed choices about their bodies.
- Preventing forced marriages and unsafe abortions.
2.4 Preventing Sexually Transmitted Diseases (STDs)
- Spreading awareness about safe sexual practices.
- Encouraging regular health checkups for early detection of STDs.
- Providing free condoms and other protective measures.
3. Key Components of a Reproductive Health Project
A strong reproductive health project includes the following essential components:
3.1 Maternal Healthcare
- Ensuring proper medical checkups during pregnancy.
- Providing essential nutrients and vitamins to pregnant women.
- Offering safe delivery services and postnatal care.
3.2 Family Planning Services
- Providing birth control education and resources.
- Encouraging responsible parenthood.
- Offering fertility treatments and reproductive assistance if needed.
3.3 Adolescent Reproductive Health
- Educating teenagers about puberty and reproductive changes.
- Raising awareness about menstrual hygiene and safe sexual behavior.
- Preventing teenage pregnancies and early marriages.
3.4 Sexual Health Education
- Teaching about reproductive organs and their functions.
- Spreading knowledge on safe sex and STD prevention.
- Promoting gender equality and healthy relationships.
4. Challenges in Implementing Reproductive Health Projects
Despite the benefits, several obstacles make it difficult to implement reproductive health projects:
4.1 Lack of Awareness and Education
- Many people, especially in rural areas, lack basic reproductive health knowledge.
- Misconceptions and myths prevent people from using family planning services.
4.2 Cultural and Religious Barriers
- Some communities oppose birth control and sex education due to traditional beliefs.
- Talking about reproductive health is considered a taboo in many places.
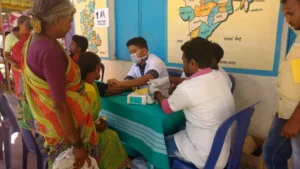
4.3 Limited Healthcare Facilities in Rural Areas
- Many villages lack hospitals or trained medical staff.
- Women often travel long distances to receive proper maternity care.
4.4 Financial and Policy Constraints
- Governments may not have enough funds to support reproductive health programs.
- Some countries do not have strong policies to protect reproductive rights.
5. Case Studies of Successful Reproductive Health Projects
5.1 India: National Health Mission
- Provides free maternal healthcare services in rural areas.
- Encourages hospital deliveries with financial incentives.
5.2 Africa: UN-Backed Health Programs
- Focuses on reducing HIV/AIDS transmission.
- Provides free contraceptives and sex education.
5.3 Latin America: Community-Based Health Models
- Trains local women as healthcare workers.
- Offers mobile clinics in remote regions.
6. Role of Technology in Reproductive Health
Technology plays a significant role in improving reproductive health services:
6.1 Telemedicine Services
- Allows women to consult doctors via phone or video calls.
- Helps those in remote areas get medical advice.
6.2 Mobile Apps for Reproductive Health
- Period-tracking apps help women understand their cycles.
- Pregnancy monitoring apps guide mothers on prenatal care.
6.3 AI and Digital Healthcare
- AI-powered diagnostics help in early detection of reproductive issues.
- Digital health records keep track of patient history.
7. Creating a Reproductive Health Project PDF
A PDF document is an effective way to share reproductive health project details. Here’s how to create a useful one:
7.1 Why PDFs are Useful
- Easy to distribute online and offline.
- Can contain text, images, and infographics.
- Accessible on mobile devices and computers.
7.2 How to Compile Data and Information
- Gather research from trusted health organizations.
- Include statistics, charts, and real-life case studies.
- Make sure the content is simple and easy to understand.
7.3 Best Practices for Designing an Engaging PDF
- Use clear headings and bullet points.
- Add pictures and illustrations to explain complex topics.
- Highlight important information with bold fonts.
8. Impact of Reproductive Health Projects on Society
Reproductive health projects have a huge impact on society, including:
8.1 Reducing Maternal and Infant Mortality
- Ensures safer pregnancies and deliveries.
- Lowers the number of pregnancy-related deaths.
8.2 Empowering Women Through Reproductive Rights
- Gives women control over their reproductive choices.
- Helps them make informed decisions about family planning.
8.3 Enhancing Economic Growth
- A healthy population leads to a stronger workforce.
- Reduces government healthcare costs in the long run.
9. Future of Reproductive Health Initiatives
The future of reproductive health will focus on:
9.1 Global Trends and Future Policies
- Governments investing more in reproductive health programs.
- Stronger laws to protect reproductive rights.
9.2 Integration into Universal Healthcare
- Making reproductive health services part of free healthcare.
- Ensuring everyone, regardless of income, gets access to care.
9.3 Role of NGOs and Government Programs
- NGOs working alongside governments to expand services.
- Public-private partnerships for better healthcare delivery.
10. Conclusion
Reproductive health is a crucial part of overall well-being. With proper awareness, accessible services, and the use of technology, reproductive health projects can transform societies by empowering individuals and ensuring safer reproductive choices. Governments, NGOs, and individuals must work together to improve reproductive health for a healthier and more prosperous future.